In the ever-evolving world of no-code tools, Browse AI has made a name for itself by simplifying web data extraction. Users can train “robots” to pull structured information from websites into spreadsheets—without writing a single line of code. Discover how Browse AI used generative AI to streamline robot training, reduce churn, and enhance the user experience with smarter automation
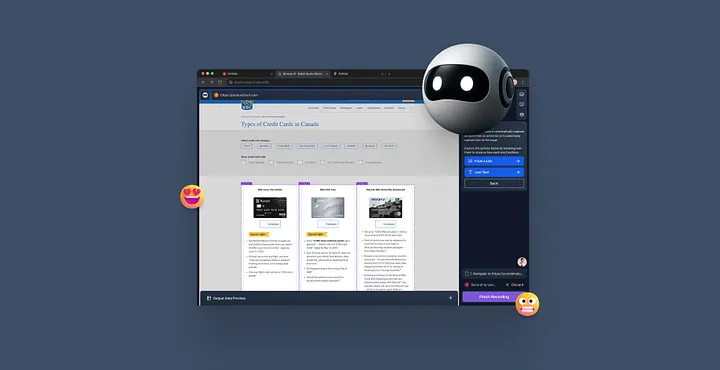
However, even with a powerful core feature, friction in the robot training experience was a persistent challenge. User confusion, manual steps, and long wait times contributed to a higher-than-expected churn rate. That’s when the Browse AI team turned to Generative AI, not to just automate but to enhance the user experience.
In this blog, we’ll break down exactly how generative AI helped us reduce churn, improve satisfaction, and deliver that delightful “AI magic” moment—all while keeping users in control.
Table of Contents
What Is Browse AI?
Browse AI is a no-code web scraping tool that enables users to extract data from websites and export it into spreadsheets or other structured formats. The core idea revolves around training a robot: users visit a page, select the data they need, and Browse AI teaches the robot how to repeat that action across similar pages.
But as elegant as the idea sounds, the original training flow wasn’t as smooth in practice. Looking to automate your web scraping with ease? Try Browse AI now — the no-code tool that lets you extract data from any website into spreadsheets with just a few clicks. Train your first robot in minutes and watch AI do the heavy lifting!
The Original Flow: How Robot Training Used to Work
Here’s a simplified breakdown of the original user journey: Want to run your trained robots across multiple inputs at once? Discover how to streamline your data extraction by learning how to Bulk-Run Tasks on Browse AI. This powerful feature allows you to automate large-scale operations efficiently, perfect for scaling your workflows with minimal effort.
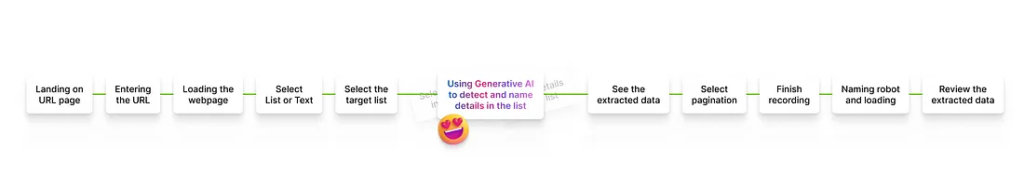
1. Enter a URL and Wait
Users started by entering a target URL. This loaded the webpage inside Browse AI’s Robot Studio, where they could begin selecting data.
Problem: The delay created ambiguity. Users weren’t sure what was happening or what to do next.
2. Select What to Extract
Users could choose from:
- Lists of items
- Individual text fields
- Screenshots
For lists, they had to:
- Select the list container
- Manually highlight each detail item
- Name each data field individually
- Define the list name, number of items, and pagination method
Problem: This was the most interaction-heavy step. Manually selecting and naming dozens of fields was time-consuming, especially for large datasets.
3. Review the Robot and Name It
Once the recording ended, Browse AI simulated the user steps and began data extraction. Meanwhile, users were asked to name the robot.
Problem: This waiting period felt uncertain and disjointed, especially if extraction was slow. Many users dropped off at this point.
Mapping the User Journey
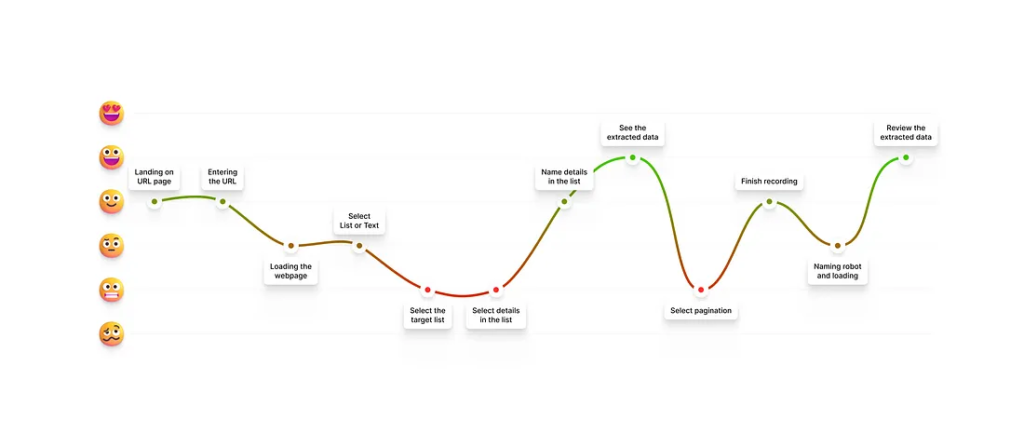
We created a user journey map, pinpointing drop-off points and frustrations. The most common complaints were:
- The tedious process of manually selecting and naming items
- Confusion around pagination settings
- Lack of clear feedback during the loading and extraction phases
It was time to rethink the experience, with Generative AI at the center. Tired of spending hours manually copying data? With Browse AI, you can automate repetitive data extraction tasks effortlessly. It’s fast, accurate, and powered by AI to make your workflow smoother than ever. Get started today and take your productivity to the next level.
Ideation: Where Generative AI Meets UX
We brainstormed several ways generative AI could help reduce friction, speed up workflows, and increase satisfaction. Here are the top ideas we explored—and how we evaluated them.
A. Full AI Auto-Detection (Rejected)

Concept: AI would automatically scan the page and decide everything:
- Whether it’s a list or text
- What items to extract
- How to label them
- How to paginate
Pros:
- Feels magical and fully automated
- Eliminates early decision-making for the user
Cons:
- Often inaccurate, leading to frustrating clean-up
- Too much info shown at once = high cognitive load
- Slower load times increased bounce rates
Verdict: Too risky and unpredictable for a first iteration.
B. AI-Powered List Item Suggestions (Selected)
Concept: When a user selects a list container, AI auto-detects the details within and assigns smart labels.
Pros:
- Targets the most common use case: list extraction
- Keeps users in control while speeding up tedious tasks
- High precision with low loading time
- Reduces naming and manual clicking
Cons:
- Occasionally includes items the user doesn’t want
Why We Chose It: This option struck the perfect balance between automation and control. It offered the biggest ROI in UX improvement with minimal risk.
The improvements to the Robot Studio speak for themselves — reduced churn, faster sessions, and smarter workflows. Want to try it for yourself? Start using Browse AI now and explore the power of intelligent automation.
C. AI for Text Extraction (On Hold)
Concept: AI would highlight all text elements on the page and assign labels.
Pros:
- Fast and magical
Cons:
- High signal-to-noise issue: too many irrelevant text fields
Verdict: Not a priority feature compared to list extraction. Placed on hold for future exploration.
D. AI for Pagination Detection (Selected)
Concept: After a list is selected, the AI attempts to detect the pagination control (such as a “Next” button) and requests user confirmation.
Pros:
- Solves a major pain point around navigation
- Reduces support requests
- Makes the experience feel smarter
Cons:
- False positives occasionally need user correction
Why We Chose It: Solved a key confusion area while enhancing user trust in the product.
What We Implemented
We moved forward with:
- B. AI List Item Suggestions
- D. AI Pagination Detection
These two features were strategically selected to address the most common friction points in the robot training experience, without overwhelming users.
The Results: Measurable UX Gains
After launching these generative AI features, we saw immediate improvements:
- Churn during robot training dropped from 43% to 36%
- Session times decreased, indicating faster completion
- Users reported the experience felt “smarter” and more seamless
Yes, some new challenges emerged: AI occasionally misidentified elements, and new UX questions were raised. But the trade-off was worth it. Users were more engaged and willing to continue interacting with the product.
What’s Next?
Based on user feedback and performance data, here are our top ideas for the next round of improvements:
1. Personalized AI Hints
Tailor AI recommendations based on page structure or domain type. For example, ecommerce product pages vs. job listings.
2. AI Confidence Scores
Show users how confident the AI is in each suggestion. This adds transparency and trust, helping users correct issues proactively.
3. Progressive AI Assistance
Rather than showing all suggestions at once, roll them out step by step. This reduces cognitive overload and improves learnability.
Key Takeaways: How Generative AI Improves UX
AI Isn’t Just About Automation
It’s about reducing user effort at the right time, in the right way.
Balance Is Everything
Too much automation creates confusion; too little makes users do unnecessary work. The sweet spot lies in supporting, not replacing, user actions.
Let the User Stay in Control
Even when AI is doing the heavy lifting, users want to feel in control. Confirmation steps, editing options, and transparency go a long way.
Final Thoughts
At Browse AI, our mission is to make web data extraction as effortless as possible. By leveraging Generative AI thoughtfully, we were able to:
- Cut down on user friction
- Reduce churn
- Boost satisfaction
- And introduce a real sense of “magic” without sacrificing usability
Generative AI isn’t a silver bullet, but when integrated with care, it can become a superpower for product teams looking to delight their users. Ready to simplify your data extraction process and reduce friction with generative AI? Browse AI is your solution. Whether you’re a marketer, analyst, or entrepreneur, this tool is built to scale with you.
👉 Sign up here and automate smarter, not harder.
Disclaimer
This article features affiliate links, which indicate that if you click on any of the links and make a purchase, we may receive a small commission. There’s no extra cost to you, and it aids in supporting our blog, enabling us to keep delivering valuable content. We solely endorse products or services that we think will benefit our audience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Browse AI?
Browse AI is a no-code platform that enables users to extract data from websites into structured formats like spreadsheets. Users train “robots” by selecting data from a webpage, which the robot then learns to replicate across similar pages.
What was the main user experience issue with Browse AI’s original robot training flow?
The original flow required users to manually select and label data, choose pagination methods, and wait through ambiguous load times. This led to confusion, frustration, and a high churn rate, particularly during the recording phase of robot training.
Why didn’t Browse AI fully automate the robot training using AI?
Full AI automation (detecting all data types and pagination without user input) was tested but ultimately rejected. It led to high cognitive load, more errors, and longer load times, which negatively impacted user experience. Users preferred to stay in control while receiving helpful AI suggestions.
What was the impact of using generative AI on user behavior?
After implementing AI-powered suggestions, Browse AI reduced its churn rate during robot training from 43% to 36%, and session times decreased. Although some AI-related issues introduced new challenges, the overall UX significantly improved.
How does AI-powered pagination detection work in Browse AI?
When a user selects a list for extraction, the AI suggests the most likely pagination method (such as clicking a “Next” button). The user can then confirm or adjust the suggestion, reducing guesswork and manual setup.